 | M. Kozlowski, J. Marciak-Kozlowska From Quarks to Bulk Matter. Physics of the Causal Thermal Phenomena, Hadronic Press, USA, 2001 |
 |
M. Kozlowski Physica Viva Dorrance Publishing Co, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2006 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Papers:
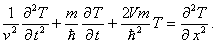 (1)
(1)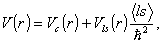 (2)
(2)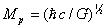 is studied. The relaxation time
and quantum diffusion coefficient for Planck gas are calculated. The new
interpretation of a Planck time,
is studied. The relaxation time
and quantum diffusion coefficient for Planck gas are calculated. The new
interpretation of a Planck time, 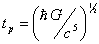 is
described. It is shown that for time period shorter than
tp the time reversal symmetry holds and for
post-Planck time the time symmetry is broken, i.e. time arrow is
created.
is
described. It is shown that for time period shorter than
tp the time reversal symmetry holds and for
post-Planck time the time symmetry is broken, i.e. time arrow is
created.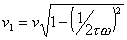 , t denotes the
relaxation time. Due to scattering the thermal wave changes the phase in
medium.
, t denotes the
relaxation time. Due to scattering the thermal wave changes the phase in
medium.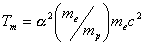 for the molecular systems is obtained with the numerical value
Tm ~ 316 K. This
temperature defines what is generally termed as the "room
temperature".
for the molecular systems is obtained with the numerical value
Tm ~ 316 K. This
temperature defines what is generally termed as the "room
temperature".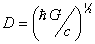 .
.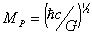 and
relaxation time equals Planck time,
and
relaxation time equals Planck time, 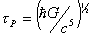 .
The quantum of thermal energy for Planck gas,
EPlanck=1019 GeV and quantum thermal
diffusion coefficient DPlanck
=(hG/c)1/2 are calculated. Within the framework of
QHT the thermal phenomena in Planck gas can be divided into two classes,
for time period shorter than tp the time reversal symmetry holds and for time
period longer than tp,
time symmetry is broken, i.e. time arrow is created.
.
The quantum of thermal energy for Planck gas,
EPlanck=1019 GeV and quantum thermal
diffusion coefficient DPlanck
=(hG/c)1/2 are calculated. Within the framework of
QHT the thermal phenomena in Planck gas can be divided into two classes,
for time period shorter than tp the time reversal symmetry holds and for time
period longer than tp,
time symmetry is broken, i.e. time arrow is created.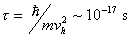 the quantum path has fractal dimension
df = 2. For Dt <
t (i.e. for attosecond laser pulses) the
quantum particle moves on straight line with velocity
vh which is equal the thermal wave velocity. In
the relativistic limit vh® c the mean free path for heat carriers is
the reduced Compton wave length
the quantum path has fractal dimension
df = 2. For Dt <
t (i.e. for attosecond laser pulses) the
quantum particle moves on straight line with velocity
vh which is equal the thermal wave velocity. In
the relativistic limit vh® c the mean free path for heat carriers is
the reduced Compton wave length 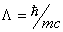 .
.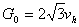 .
.
 about us about us |
 research projects research projects |
 interests interests |
 publications publications |
 notes notes |
 links links |

 home
home