


Next: Limiting cases
Up: Odd-even staggering of binding
Previous: Odd-even staggering filters
Theoretical models
In this section, we investigate several exactly solvable models to see
the interplay between the particle-hole and particle-particle channels
of interaction.
In all cases, the Hamiltonian has the form
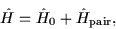 |
(13) |
where
 is either the intrinsic (i.e., deformed)
single-particle Hamiltonian or the
laboratory-system quadrupole-quadrupole
Hamiltonian, and
is either the intrinsic (i.e., deformed)
single-particle Hamiltonian or the
laboratory-system quadrupole-quadrupole
Hamiltonian, and
 is always the monopole-pairing
(seniority) Hamiltonian:
is always the monopole-pairing
(seniority) Hamiltonian:
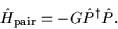 |
(14) |
In Eq. (14) G is the pairing strength parameter,
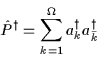 |
(15) |
denotes the monopole-pair creation operator, and  denotes
the time-reversed state.
denotes
the time-reversed state.
Properties of the Hamiltonian (13) depend on the ratio
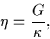 |
(16) |
where  represents the strength of
represents the strength of  .
For both
.
For both  (weak pairing) and
(weak pairing) and  (strong pairing),
one can treat the Hamiltonian (13) perturbatively. However,
the situation encountered most often in the nuclear physics context
is the intermediate case (
(strong pairing),
one can treat the Hamiltonian (13) perturbatively. However,
the situation encountered most often in the nuclear physics context
is the intermediate case (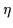
 0.4) in which
pairing correlations are strongly influenced by the nuclear mean field.
0.4) in which
pairing correlations are strongly influenced by the nuclear mean field.



Next: Limiting cases
Up: Odd-even staggering of binding
Previous: Odd-even staggering filters
Jacek Dobaczewski
2000-03-09