Triple threshold lasing from a photonic trap in a Te/Se-based optical microcavity
K. Sawicki, J.-G. Rousset, R. Rudniewski, W. Pacuski, M. Ściesiek, T. Kazimierczuk, K. Sobczak, J. Borysiuk, M. Nawrocki, and J. Suffczyński
Communications Physics 2, 38, 2019
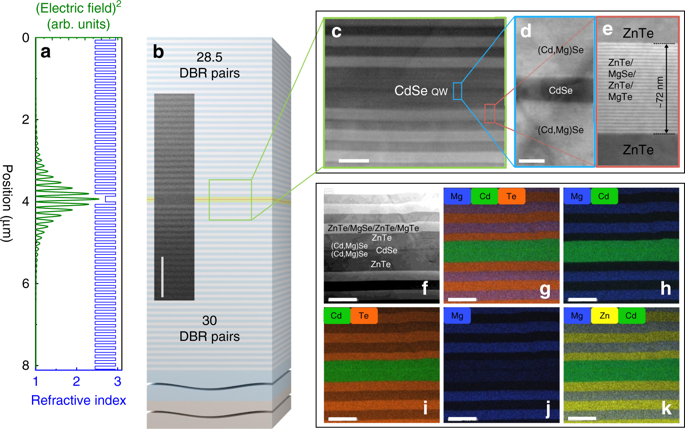
Lasing relies on light amplification in the active medium of an optical resonator. There are three lasing regimes in the emission from a quantum well coupled to a semiconductor microcavity. Polariton lasing in the strong light–matter coupling regime arises from the stimulated scattering of exciton-polaritons. Photon lasing in the weak coupling regime relies on either of two mechanisms: the stimulated recombination of excitons, or of an electron–hole plasma. So far, only one or two out of these three regimes have been reported for a given structure, independently of the material system studied. Here, we report on all three lasing regimes and provide evidence for a three-threshold behavior in the emission from a photonic trap in a Se/Te-based planar microcavity comprising a single CdSe/(Cd,Mg)Se quantum well. Our work establishes the so far unsettled relation between lasing regimes that differ by their light-matter coupling strength and degree of electron–hole Coulomb correlation.
(Cd,Zn,Mg)Te-based microcavity on MgTe sacrificial buffer: Growth, lift-off, and transmission studies of polaritons
B. Seredyński, M. Król, P. Starzyk, R. Mirek, M. Ściesiek, K. Sobczak, J. Borysiuk, D. Stephan, J.-G. Rousset, J. Szczytko, B. Piętka, and W. Pacuski
Phys. Rev. Materials 2, 043406, 2018
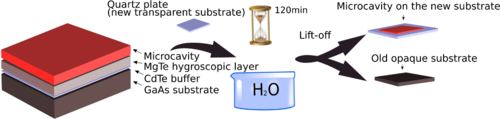
Opaque substrates precluded, so far, transmission studies of II-VI semiconductor microcavities. This work presents the design and molecular beam epitaxy growth of semimagnetic (Cd, Zn, Mn) Te quantum wells embedded into a (Cd, Zn, Mg) Te-based microcavity, which can be easily separated from the GaAs substrate. Our lift-off process relies on the use of a MgTe sacrificial layer which stratifies in contact with water. This allowed us to achieve a II-VI microcavity prepared for transmission measurements. We evidence the strong light-matter coupling regime using photoluminescence, reflectivity, and transmission measurements at the same spot on the sample. By comparing a series of reflectance spectra before and after lift-off, we prove that the microcavity quality remains high. Thanks to Mn content in quantum wells we show the giant Zeeman splitting of semimagnetic exciton-polaritons in our transmitting structure.
Design and control of mode interaction in coupled ZnTe optical microcavities
M. Ściesiek, W. Pacuski, J-G. Rousset, M. Parlińska-Wojtan, A. Golnik, J. Suffczyński
Crystal Growth & Design 17 (7), 3716, 2017
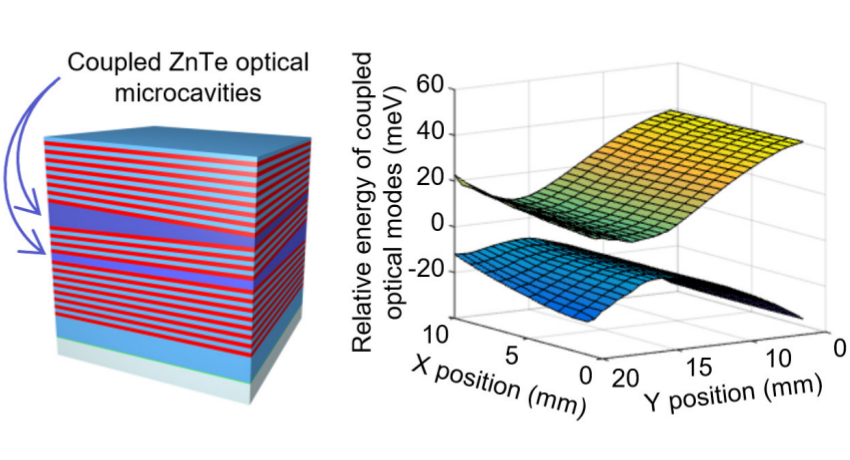
The photonics involving II-VI epitaxial layers was limited so far to structures based on a single planar microcavity. Here, we present double, vertically coupled, ZnTe optical microcavities in planar and 3-D photonic molecule geometry. We design the structures with the help of transfer matrix method calculations and we establish their fabrication technology by molecular beam epitaxy. We characterize the samples by reflectivity spatial mapping and study them by measurements of angle-integrated and angle-resolved photoluminescence and reflectivity. We efficiently tailor the interaction strength of the cavities optical modes by an adjustment of the spatial separation between the microcavities, their thickness ratio and by the size of micropillars etched out of the planar structure. Coupling constants extracted from our measurements agree well with those determined in calculations in the frame of a tight-binding approach applied to one-dimensional photonic structures.
Effect of electron-hole separation on optical properties of individual Cd(Se,Te) Quantum Dots
M. Ściesiek, J. Suffczyński, W. Pacuski, M. Parlińska-Wojtan, T. Smoleński, P. Kossacki A. Golnik
Physical Review B 93 (19), 195313, 2016
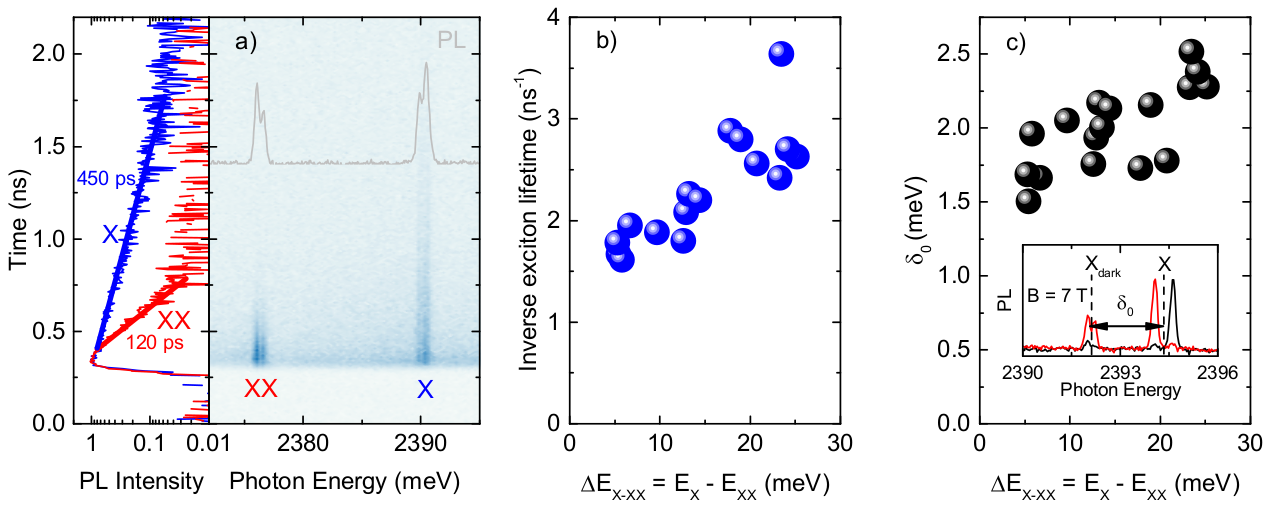
Cd(Se,Te) quantum dots (QDs) in a ZnSe barrier typically exhibit a very high spectral density, which precludes investigation of single dot photoluminescence. We design, grow, and study individual Cd(Se,Te)/ZnSe QDs of low spectral density of emission lines achieved by the implementation of Mn-assisted epitaxial growth. We find an unusually large variation of exciton-biexciton energy difference (3meV≤ΔEX−XX≤26 meV) and of exciton radiative recombination rate in the statistics of QDs. We observe a strong correlation between the exciton-biexciton energy difference, exciton recombination rate, splitting between dark and bright excitons, and additionally the exciton fine-structure splitting δ1 and the Landé factor. The above results indicate that the values of the δ1 and of the Landé factor in the studied QDs are dictated primarily by the electron and hole respective spatial shift and wave functions overlap, which vary from dot to dot due to a different degree of localization of electrons and holes in, respectively, CdSe- and CdTe-rich QD regions.
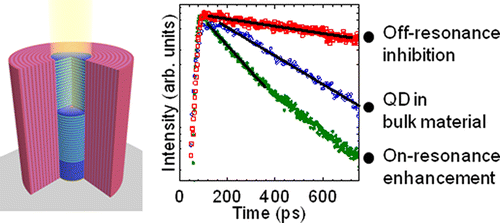
Inhibition and enhancement of the spontaneous emission of quantum dots in micropillar cavities with radial distributed Bragg reflectors
T. Jakubczyk, H. Franke, T. Smoleński, M. Ściesiek, W. Pacuski, A. Golnik, R. Schmidt-Grund, M. Grundmann, C. Kruse, D. Hommel, P. Kossacki
ACS nano 8 (10), 9970-9978, 2014
We present a micropillar cavity where nondesired radial emission is inhibited. The photonic confinement in such a structure is improved by implementation of an additional concentric radial-distributed Bragg reflector. Such a reflector increases the reflectivity in all directions perpendicular to the micropillar axis from a typical value of 15–31% to above 98%. An inhibition of the spontaneous emission of off-resonant excitonic states of quantum dots embedded in the microcavity is revealed by time-resolved experiments. It proves a decreased density of photonic states related to unwanted radial leakage of photons out of the micropillar. For on-resonance conditions, we find that the dot emission rate is increased, evidencing the Purcell enhancement of spontaneous emission. The proposed design can increase the efficiency of single-photon sources and bring to micropillar cavities the functionalities based on lengthened decay times.
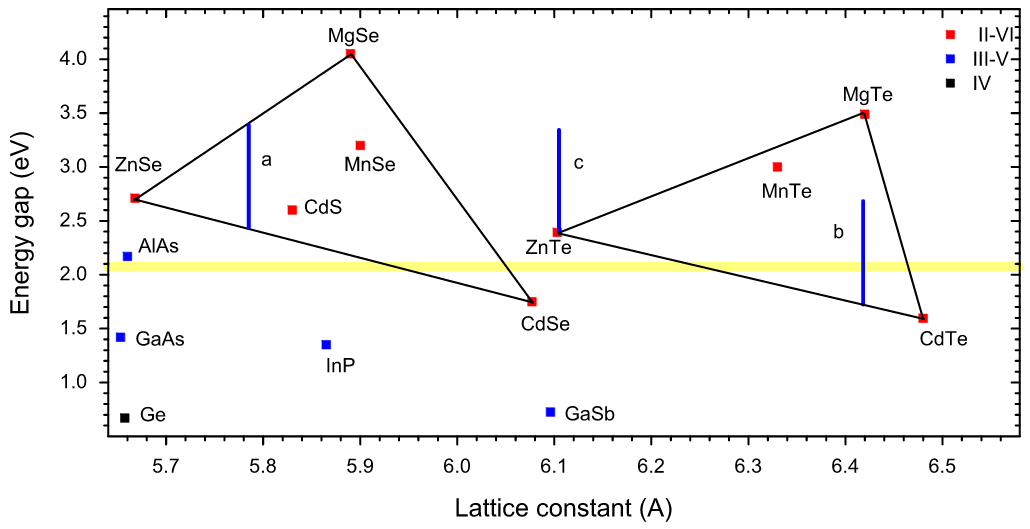
MBE grown microcavities based on seleium and tellurium compounds
J-G. Rousset, J. Kobak, E. Janik, T. Jakubczyk, R. Rudniewski, P. Piotrowski, M. Ściesiek, J. Borysiuk, T. Słupiński, A. Golnik, P. Kossacki, M. Nawrocki, W. Pacuski
Journal of Crystal Growth 401, 499-503, 2014
In this work, we present three groups of microcavities: based on selenium compounds only, based on tellurium compounds only, and structures based on mixed selenium and tellurium compounds. We focus on their possible applications in the field of optoelectronic devices and fundamental physics (VCSELs, narrow range light sources, studies of cavity-polariton electrodynamics) in a range of wavelength from 540 to 760 nm.
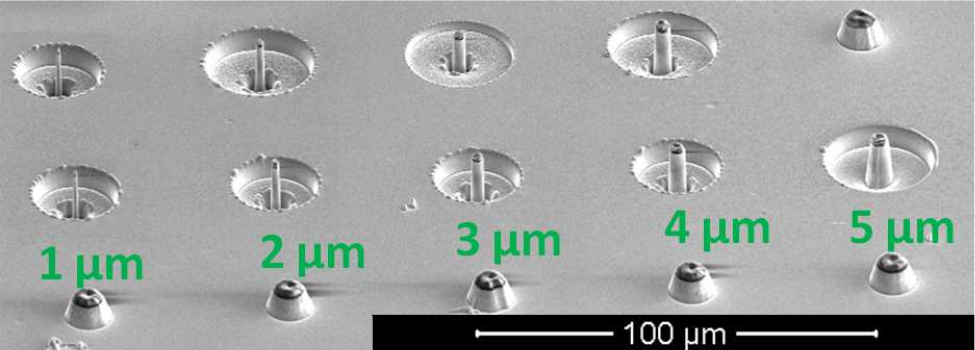
Toward Better Light-Confinement in Micropillar Cavities
M. Ściesiek, K. Gietka, A. Golnik, T. Jakubczyk, W. Pacuski, C. Kruse, D. Hommel
Acta Physica Polonica A 120 (5), 877-879, 2011
We report on a two-step etching of ZnTe based micropillars. We demonstrate applicability of the technology and we analyze the optical properties of obtained structures. Microphotoluminescence spectra of individual micropillars show a typical mode pattern that confirms a successful growth of photonic structures. The reflectivity and photoluminescence spectra of a planar microcavity measured for various incident angles show that additional side distributed Bragg reflectors will be important for the further enhancement of photon confinement in micropillar cavity.