Next: Intrinsic average particle number
Up: Skyrme HFB+VAPNP procedure: practical
Previous: Two kinds of nucleons
The canonical-basis single-particle wave functions,
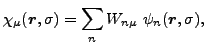 |
(75) |
are defined by the unitary matrix  which diagonalizes the density matrices,
which diagonalizes the density matrices,
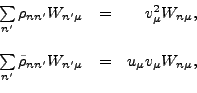 |
(76) |
where  are the occupation probabilities
are the occupation probabilities
 and
and
 .
In the canonical representation, the gauge-angle-dependent matrices become
diagonal with the diagonal matrix elements given by:
.
In the canonical representation, the gauge-angle-dependent matrices become
diagonal with the diagonal matrix elements given by:
and the determinant of matrix
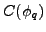 , needed in
Eq. (40), becomes a product of the diagonal values (77).
The use of the canonical representation significantly
simplifies calculations of the projected fields.
, needed in
Eq. (40), becomes a product of the diagonal values (77).
The use of the canonical representation significantly
simplifies calculations of the projected fields.
Jacek Dobaczewski
2006-10-13