


Next: Canonical representation
Up: Skyrme HFB+VAPNP procedure: practical
Previous: Skyrme HFB+VAPNP procedure: practical
As one is dealing with  protons and
protons and  neutrons, two gauge angles,
neutrons, two gauge angles,
 and
and  , must enter
the number projection operator:
, must enter
the number projection operator:
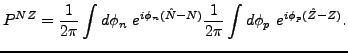 |
(70) |
Consequently, the total projected energy (53) becomes
a double integral,
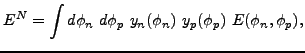 |
(71) |
where the transition energy density
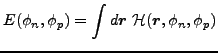 |
(72) |
depends on both gauge angles  ,
,  .
.
To simplify notation, we use the isospin
label  =
= (
( =+1 for neutrons and -1 for protons)
and
=+1 for neutrons and -1 for protons)
and  =
= . In the following, we shall employ the convention
. In the following, we shall employ the convention
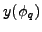

 ,
,
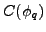

 ,
and
,
and
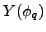

 .
The isospin-dependent particle-hole and
particle-particle fields (66), (67) can be written as:
.
The isospin-dependent particle-hole and
particle-particle fields (66), (67) can be written as:
In numerical applications, the two-dimensional integrals
over the gauge angles are replaced by a sum over
 points
using the Gauss-Chebyshev
quadrature method [34].
points
using the Gauss-Chebyshev
quadrature method [34].



Next: Canonical representation
Up: Skyrme HFB+VAPNP procedure: practical
Previous: Skyrme HFB+VAPNP procedure: practical
Jacek Dobaczewski
2006-10-13
![]() protons and
protons and ![]() neutrons, two gauge angles,
neutrons, two gauge angles,
![]() and
and ![]() , must enter
the number projection operator:
, must enter
the number projection operator:
![]() =
=![]() (
(![]() =+1 for neutrons and -1 for protons)
and
=+1 for neutrons and -1 for protons)
and ![]() =
=![]() . In the following, we shall employ the convention
. In the following, we shall employ the convention
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
,
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
and
,
and
![]()
![]()
![]() .
The isospin-dependent particle-hole and
particle-particle fields (66), (67) can be written as:
.
The isospin-dependent particle-hole and
particle-particle fields (66), (67) can be written as: