


Next: Input data file
Up: Modifications introduced in version
Previous: Calculation of moments and
Calculation of the Bohr deformation parameters
In version (v1.75r), the Bohr deformation parameters
 [5] are calculated using the
first-order approximation. The code uses the simplest
linearized expression (cf. Eq. (1.35) of Ref. [5]) relating
deformation parameters to multipole moments of a sharp-edge uniformly
charged shape, i.e.,
[5] are calculated using the
first-order approximation. The code uses the simplest
linearized expression (cf. Eq. (1.35) of Ref. [5]) relating
deformation parameters to multipole moments of a sharp-edge uniformly
charged shape, i.e.,
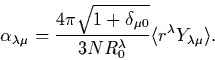 |
(1) |
For 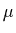
 0 the deformation parameters contain the standard factor of
0 the deformation parameters contain the standard factor of
 .
This reflects the fact that for the assumed
.
This reflects the fact that for the assumed  simplex
symmetry (see Sec. 3.1 of I), the values of multipole moments
for
simplex
symmetry (see Sec. 3.1 of I), the values of multipole moments
for 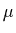 <0 are up to a phase equal to those for
<0 are up to a phase equal to those for 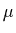 >0.
Neutron, proton, or mass deformation parameters are calculated from the
corresponding neutron, proton, or mass multipole moments
>0.
Neutron, proton, or mass deformation parameters are calculated from the
corresponding neutron, proton, or mass multipole moments
 ,
and by setting N in Eq. (3) equal to the number of neutrons, protons,
or nucleons. The equivalent radii R0 are respectively calculated from
the neutron, proton, or mass rms radii as
,
and by setting N in Eq. (3) equal to the number of neutrons, protons,
or nucleons. The equivalent radii R0 are respectively calculated from
the neutron, proton, or mass rms radii as
 .
One should note that for large
deformations the neglected higher-order terms (see Eq. (1.35) of
Ref. [5]) will in general be non-negligible. Therefore, the
printed values of the Bohr deformation parameters should be used only as
(often very) rough estimates.
.
One should note that for large
deformations the neglected higher-order terms (see Eq. (1.35) of
Ref. [5]) will in general be non-negligible. Therefore, the
printed values of the Bohr deformation parameters should be used only as
(often very) rough estimates.



Next: Input data file
Up: Modifications introduced in version
Previous: Calculation of moments and
Jacek Dobaczewski
2000-03-01
![]() [5] are calculated using the
first-order approximation. The code uses the simplest
linearized expression (cf. Eq. (1.35) of Ref. [5]) relating
deformation parameters to multipole moments of a sharp-edge uniformly
charged shape, i.e.,
[5] are calculated using the
first-order approximation. The code uses the simplest
linearized expression (cf. Eq. (1.35) of Ref. [5]) relating
deformation parameters to multipole moments of a sharp-edge uniformly
charged shape, i.e.,