


Next: Direct interaction energy
Up: The Negele-Vautherin density matrix
Previous: Introduction
Local energy density for spinless particles of one kind
In this section, we consider the simplest (and academic) case of fermions
with no spin and no isospin.
First we recall that for an arbitrary non-local finite-range interaction
 ,
the Kohn-Sham interaction energy [21] has the form
,
the Kohn-Sham interaction energy [21] has the form
whereas for a local interaction,
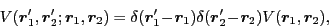 |
(2) |
the interaction energy reduces to:
where
 and
and
 are local densities.
As is well known, the first term in Eq. (3) (the direct term)
depends only on local densities, whereas the second one (the exchange term)
depends on the modulus squared of the non-local density. This markedly
different structure of the two terms requires separate treatment,
as discussed in the following two subsections.
are local densities.
As is well known, the first term in Eq. (3) (the direct term)
depends only on local densities, whereas the second one (the exchange term)
depends on the modulus squared of the non-local density. This markedly
different structure of the two terms requires separate treatment,
as discussed in the following two subsections.
Subsections



Next: Direct interaction energy
Up: The Negele-Vautherin density matrix
Previous: Introduction
Jacek Dobaczewski
2010-03-07
![]() ,
the Kohn-Sham interaction energy [21] has the form
,
the Kohn-Sham interaction energy [21] has the form
