Press releases
Much like white light, spacetime is also composed of a certain rainbow
2016-01-14
When white light is passed through a prism, the rainbow on the other side reveals a rich palette of colors. Theorists from the Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw have shown that in models of the Universe using any of the quantum theories of gravity there must also be a 'rainbow' of sorts, composed of different versions of spacetime. The mechanism predicts that instead of a single, common spacetime, particles of different energies essentially sense slightly modified versions thereof. | More...
Perfectly accurate clocks turn out to be impossible
2015-10-07
Can the passage of time be measured precisely, always and everywhere? The answer will upset many watchmakers. A team of physicists from the universities of Warsaw and Nottingham have just shown that when we are dealing with very large accelerations, no clock will actually be able to show the real passage of time, known as “proper time”. | More...
Ultrafast Lasers of the Future Will Be Compact and Smart
2015-09-23
Today’s lasers generating ultrashort light pulses require major and complex optical systems that measure pulse parameters or tune their wavelength. As part of the EU MINIMODS project, the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw has achieved significant miniaturisation of laser diagnostics systems. The achievement paves the way for industrial production of femtosecond lasers with a compact construction that are reliable and potentially capable of self-calibration. | More...
Our view inside the atomic nucleus just got a whole lot clearer
2015-09-09
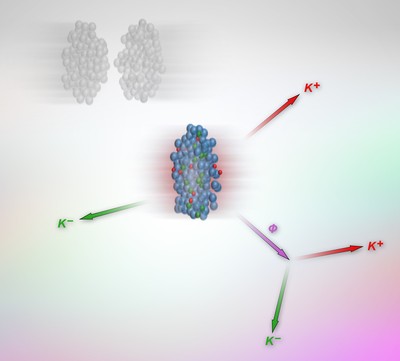
How can we know what is going on inside atomic nuclei? One important source of information comes from mesons, particles emitted during nuclear collisions. But until now it was not clear which mesons are actually carrying reliable information about a nucleus, and which ones were only interfering. Warsaw University physicists have published a careful analysis of data gathered by the international FOPI collaboration, which makes our ability to peer inside the atomic nucleus much more transparent. | More...
Small, inexpensive, and incredibly resilient: a new femtosecond laser for industry
2015-08-19
A team at the University of Warsaw, Faculty of Physics has created a laser capable of generating ultrashort pulses of light even under extremely difficult external conditions. This unique combination of precision and resilience is due to the fact that the whole process of generating femtosecond laser pulses takes place within a specially-selected optical fiber. | More...
Quantum ‘paparazzi’ film photons in the act of pairing up
2015-04-22
In the quantum world of light, being distinguishable means staying lonely. Only those photons that are indistinguishable can wind up in a pair, through what is called Hong-Ou-Mandel interference. This subtle quantum effect has been successfully imaged for the first time by two doctoral students from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw.
Top-precision optical atomic clock starts ticking
2015-02-25
A state-of-the-art optical atomic clock, collaboratively developed by scientists from the University of Warsaw, Jagiellonian University, and Nicolaus Copernicus University, is now “ticking away” at the National Laboratory of Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics in Toruń, Poland. As the first of its kind in Poland and one of just a handful of clocks of this caliber in the world, the new clock will keep track of the passage of time with extraordinary precision.
Getting a grip on exotic atomic nuclei
2015-02-18
A new model describing atomic nuclei, proposed by a physicist from the University of Warsaw Faculty of Physics, more accurately predicts the properties of various exotic isotopes that are created in supernova explosions or inside nuclear reactors.
Only the Lonely… (Reveal the Secrets of Atomic Nuclei)
2015-01-21
Individual protons and neutrons in atomic nuclei turn out not to behave according to the predictions made by existing theoretical models. This surprising conclusion, reached by an international team of physicists including staff members from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw (UW), forces us to reconsider how we have been describing large atomic nuclei for the past several decades.
Global Quantum Communications – No Longer the Stuff of Fiction?
2014-11-26
Neither quantum computers nor quantum cryptography will become prevalent technologies without memory systems able to manipulate quantum information easily and effectively. The Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw has recently made inroads into popularizing quantum information technologies by creating an atomic memory with outstanding parameters and an extremely simple construction.