Press releases
Large groups of individual photons now available on demand – an equivalent of photonic ‘integrated circuit’
2017-02-08
Holographic atomic memory, invented and constructed by physicists from the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, is the first device able to generate single photons on demand in groups of several dozen or more. The device, successfully demonstrated in practice, overcomes one of the fundamental obstacles towards the construction of some type of quantum computer | More
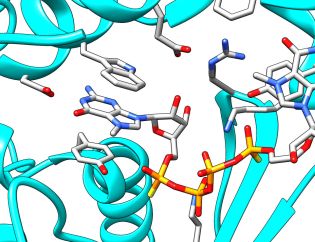
Towards therapeutic applications of mRNA: new insights into translation and decapping
2016-11-30
Gene therapy gives hope to millions of patients. Researchers from the University of Warsaw have been working on mRNA containing a modified fragment which initiates protein biosynthesis. Recently published results reveal that new compounds – designed and synthesized at the University of Warsaw – are more stable and effective than their natural equivalents, and their synthesis is simpler. The compounds allow scientists to gain a better understanding of the mechanisms of protein biosynthesis in cells, which in turn should help them design better therapeutics | More
Single photon converter – a key component of quantum internet
2016-11-22
A Polish-British team of physicists has constructed and tested a compact, efficient converter capable of modifying the quantum properties of individual photons. The new device should facilitate the construction of complex quantum computers, and in the future may become an important element in global quantum networks, the successors of today’s Internet | More
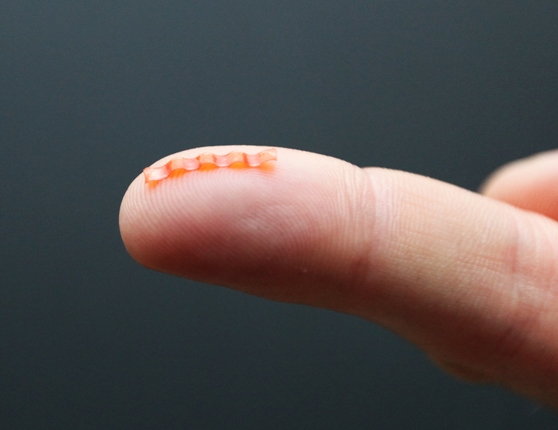
Natural scale caterpillar soft robot is powered and controlled with light
2016-08-18
Researchers at the Faculty of Physics at the University of Warsaw, using the liquid crystal elastomer technology, originally developed in the LENS Institute in Florence, demonstrated a bioinspired micro-robot capable of mimicking caterpillar gaits in natural scale. The 15-millimeter long soft robot harvests energy from green light and is controlled by spatially modulated laser beam. Apart from travelling on flat surfaces, it can also climb slopes, squeeze through narrow slits and transport loads. | More
The “Big Bang” of the Internet in Poland occurred exactly a quarter-century ago, initiated by scientists from the University of Warsaw’s Faculty of Physics
2016-08-17
The Internet, a powerful tool for shaping the world and societies, first took root in Poland a quarter-century ago, starting from a landmark email sent from the University of Warsaw’s Faculty of Physics. Today, it can be found in almost every pocket or purse in Poland. How did the Internet explode into the Polish mainstream?
Today marks a beautiful anniversary: the Internet in Poland is celebrating its silver jubilee. On 17 August 1991, a short yet historically significant email was sent from the pavilion in front of the building of the University of Warsaw’s Faculty of Physics on 69 Hoża Street in Warsaw to the DESY laboratory in Hamburg, Germany.
Safer air travel: existing navigation data can help pilots avoid turbulence
2016-08-10
Detecting turbulence remains the Achilles' heel of modern-day aviation. The reports submitted by pilots, subjective and often very inaccurate, are the least expensive and the most frequently used method for trying to predict where it will occur. Scientists from the Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw, have demonstrated that turbulence can be detected in a much faster and more precise way, using data already routinely broadcast by the aircraft operated by commercial airlines | More
Polish muon hunters increase the research potential of the LHC
2016-07-27
As the beams of the LHC accelerator start colliding at maximum energies, the detectors become inundated by a flow of secondary particles, including muons. The challenging task of quickly identifying the most interesting collisions within the CMS detector, one of the main experiments at the LHC, is handled by a special selection system. Having been recently revamped and modernized by physicists and engineers from Poland, the system is now playing a key role in the search for new physical phenomena | More
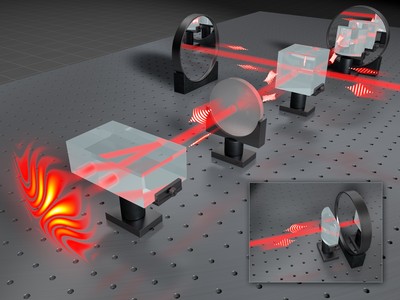
The birth of quantum holography: Making holograms of single light particles!
2016-07-18
Until quite recently, creating a hologram of a single photon was believed to be impossible due to fundamental laws of physics. However, scientists at the Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw, have successfully applied concepts of classical holography to the world of quantum phenomena. A new measurement technique has enabled them to register the first ever hologram of a single light particle, thereby shedding new light on the foundations of quantum mechanics | More
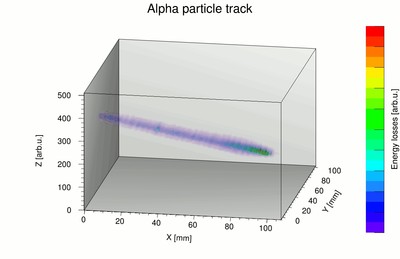
At the cradle of oxygen: Brand-new detector to reveal the interiors of stars
2016-06-02
The most intense source of gamma radiation constructed to date will soon become operational at the ELI Nuclear Physics research facility. It will be possible to study reactions that reveal the details of many processes occurring within stars, in particular those leading to the formation of oxygen. An important part of the equipment will rely on a particle detector built by physicists at the University of Warsaw. A prototype has recently concluded the first round of testing. | More
The strain allows to control the magnetic properties of individual iron atom
2016-01-28
The iron Fe2+ atom embedded in a semiconductor exhibits a single non-degenerate ground state of zero magnetic moment. A team of scientists from the University of Warsaw has just shown that by using sufficiently large strain it is possible to tailor the energy spectrum of the iron atom to obtain doubly degenerate (magnetic) ground state. Such a state can be utilized for storage and processing of the quantum information. This discovery has been just published in prestigious research journal of Nature Communications [T. Smoleński et al., Nature Commun. 7, 10484 (2016)] | More...